AI Compliance Audit: Mastering the EU AI Act and Global AI Regulations
Introduction: The Rising Importance of AI Compliance
In 2025, as governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are establishing frameworks to govern AI systems, with the European Union leading through its groundbreaking EU AI Act. An AI compliance audit is no longer optional, it’s essential for organizations aiming to mitigate risks, improve trust, and avoid legal penalties.
What is an AI Compliance Audit?
An AI compliance audit is a structured assessment process that evaluates whether AI systems comply to relevant laws, ethical standards, and risk management protocols. These audits cover areas such as data privacy, algorithmic transparency, bias mitigation, and accountability. With regulations like the EU AI Act setting precedents, audits ensure that AI technologies operate within defined legal and ethical boundaries.
Overview of the EU AI Act: A Global Benchmark
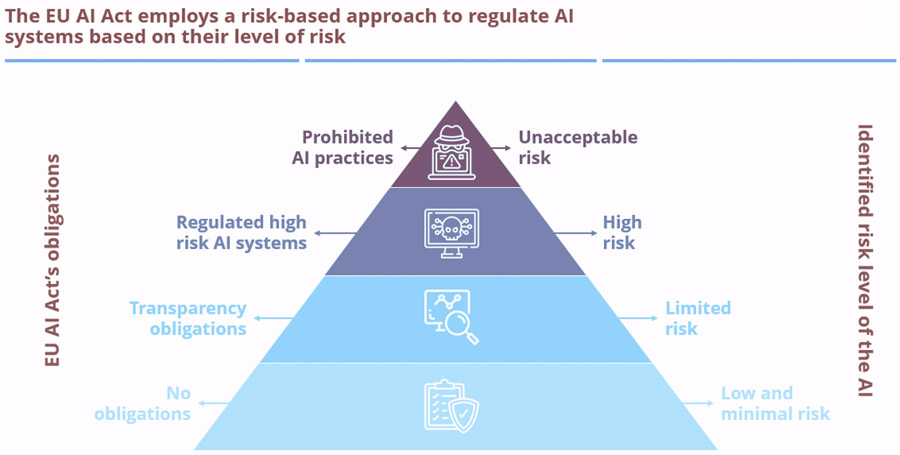
The EU AI Act is the world’s first fully comprehensive regulatory framework dedicated to artificial intelligence. Adopted to ensure the safe and trustworthy deployment of AI, the Act classifies AI systems into three distinct risk categories:
- Unacceptable Risk:AI applications that threaten fundamental rights (e.g., social scoring systems) are outright banned.
- High-Risk AI:Systems used in critical sectors like healthcare, employment, and law enforcement must meet stringent compliance obligations, including transparency, human oversight, and robustness.
- Minimal or Limited Risk:Most AI applications, such as AI-driven recommendation engines, are largely unregulated but encouraged to follow voluntary codes of conduct.
Much like the GDPR, which transformed global data privacy practices, the EU AI Act is poised to influence AI governance worldwide, encouraging countries and organizations to align with its principles.
Key Compliance Requirements Under the EU AI Act
For organizations, deploying high-risk AI systems, the EU AI Act outlines several mandatory compliance requirements. These include:
- Risk Management System:Implementing continuous risk assessment throughout the AI system’s lifecycle.
- Data Governance:Ensuring high-quality, bias-free datasets to prevent discriminatory outcomes.
- Technical Documentation:Maintaining detailed records to demonstrate compliance with regulatory standards like EU AI ACT, NIST.
- Transparency Obligations:Informing users when they are interacting with AI systems.
- Human Oversight:Designing systems that allow human intervention to prevent or minimize risks.
- Robustness and Accuracy:Ensuring AI systems perform reliably under intended conditions.
Failure to comply with the regulation can result in significant penalties, with fines reaching up to €35 million or 7% of global annual turnover, whichever is higher.
AI Governance Frameworks Beyond the EU: A Global Perspective
While the EU AI Act is pioneering, other regions are also developing AI governance frameworks:
- United States:The Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights emphasizes ethical AI principles but lacks binding legislation.
- Canada:The proposed Artificial Intelligence and Data Act (AIDA) focuses on risk management and accountability.
- China:Enforces strict regulations on algorithmic recommendation services and deep synthesis technologies.
- OECD AI Principles:Adopted by 46 countries, promoting responsible stewardship of trustworthy AI.
Organizations operating globally must stay informed about overlapping and divergent compliance obligations to avoid regulatory shortfalls.
Conducting an Effective AI Compliance Audit: Step-by-Step
Executing a thorough AI compliance audit involves a structured approach:
- Identify Applicable Regulations:Determine which laws, like the EU AI Act, apply to your AI systems based on geography and use case.
- Classify AI Systems by Risk:Use frameworks to categorize AI tools into risk levels (e.g., high-risk, Limited risk).
- Assess Data Practices:Review data sourcing, management, and governance for compliance with fairness and privacy standards like GDPR.
- Evaluate Algorithmic Transparency:Ensure AI decision-making processes are explainable and auditable.
- Implement Controls and Mitigation:Apply necessary technical and organizational safeguards.
- Document Compliance Efforts:Maintain comprehensive records for regulatory review.
- Engage in Continuous Monitoring:AI compliance is not a one-time task; establish regular audits and updates.
This proactive auditing process helps organizations demonstrate accountability and build stakeholder trust.
The Role of AI Risk Classification in Compliance Audits
Risk classification is the foundation of any AI compliance audit. The EU AI Act mandates that organizations assess their AI systems against predefined risk levels. This classification determines the extent of regulatory obligations:
- Unacceptable Risk:Immediate prohibition of the AI system like public facial recognition systems.
- High Risk:Requires strict adherence to compliance protocols.
- Limited Risk:Transparency obligations, such as notifying users they are interacting with AI.
- Minimal Risk:No mandatory requirements but encouraged ethical practices.
Accurate classification not only ensures legal compliance but also aligns AI deployment with ethical standards, reducing reputational risks.
Tools and Technologies Supporting AI Compliance Audits
To streamline the complex process of auditing AI systems, various tools and platforms have emerged:
- AI Act Compliance Checker:A tool designed to help organizations assess obligations under the EU AI Act.
- Algorithmic Auditing Software:Solutions like IBM’s AI Fairness 360 or Google’s What-If Tool assist in identifying bias and fairness issues.
- Data Governance Platforms:Tools such as Collibra and Talend ensure data quality and traceability for compliant AI training datasets.
- Model Explainability Frameworks:SHAP and LIME provide insights into AI decision-making processes, supporting transparency requirements.
Leveraging these technologies enhances audit efficiency, accuracy, and ensures continuous compliance with evolving AI regulations.
Challenges in Implementing AI Compliance Audits
Despite the availability of frameworks and tools, organizations face several challenges when conducting audits:
- Complexity of AI Systems:Advanced AI models, such as deep learning, often operate as “black boxes,” complicating transparency efforts.
- Dynamic Regulatory Landscape:With AI laws rapidly evolving, staying updated on compliance requirements is a continuous effort.
- Cross-Border Compliance:Global operations require adherence to multiple, sometimes conflicting, regulatory frameworks.
- Resource Constraints:SMEs may lack the expertise or budget to implement comprehensive audit processes.
- Data Privacy Concerns:Balancing AI performance with data protection obligations, especially under GDPR, adds additional layers of complexity.
Addressing these challenges requires a strategic approach, combining legal expertise, technical solutions, and a culture of ethical AI development.
Best Practices for Achieving AI Compliance
To navigate the complexities of AI regulations like the EU AI Act, organizations should adopt industry recognized best practices:
- Integrate Compliance Early:Incorporate regulatory considerations during the AI design and development phases (Ethics by Design).
- Establish a Governance Framework:Create cross-functional teams involving legal, technical, and operational stakeholders to oversee AI compliance.
- Conduct Regular Training:Educate staff on AI ethics, data privacy, and compliance requirements to promote a culture of accountability.
- Engage Third-Party Auditors:Leverage independent assessments to validate internal compliance efforts and uncover blind spots.
Proactive adherence to these practices not only ensures compliance but also enhances organizational reputation and stakeholder trust.
The Impact of Non-Compliance: Legal and Financial Risks
Ignoring AI compliance audit obligations can lead to severe consequences under EU AI Act:
- Hefty Fines:Penalties can reach up to €35 million or 7% of global annual turnover for breaches involving high-risk AI systems.
- Operational Disruptions:Non-compliant AI systems may be banned or require costly modifications, halting business operations.
- Reputational Damage:Publicized violations can erode customer trust and investor confidence.
- Legal Actions:Organizations may face lawsuits from affected individuals or advocacy groups over AI misuse or bias.
Compliance is not merely a regulatory checkbox but a critical risk management strategy safeguarding both financial stability and brand integrity.
The Future of AI Compliance: Emerging Trends and Developments
The landscape of AI audits is poised for significant evolution as AI technologies advance and regulatory frameworks mature:
- Global Harmonization:Efforts are underway to align AI regulations across jurisdictions, reducing complexity for multinational organizations.
- Focus on General-Purpose AI (GPAI):The EU AI Act and other bodies are developing guidelines for large language models and foundational AI systems.
- Automated Compliance Tools:AI-driven solutions will increasingly assist in real-time compliance monitoring and reporting.
- Stronger Ethical Standards:Beyond legal compliance, organizations will adopt ethical AI frameworks to address societal impacts.
- Dynamic Risk Assessment:Continuous risk evaluation will replace static compliance checks, ensuring AI systems adapt to changing regulatory environment.
Staying ahead of these trends will be essential for organizations aiming to leverage AI responsibly and competitively.
Conclusion: Embracing AI Compliance as a Strategic Advantage
In this today’s world, where artificial intelligence shapes critical aspects of business and society, AI audits have become necessary. Frameworks like the EU AI Act, NIST set the tone for responsible AI governance, emphasizing transparency, accountability, and risk management.
Organizations that proactively adopt robust compliance strategies not only mitigate legal and financial risks but also position themselves as leaders in ethical AI innovation. By embedding compliance into their core operations, businesses can improve trust, enhance brand value, and ensure sustainable AI deployment in a rapidly evolving regulatory environment.
FAQs About AI Compliance Audit and the EU AI Act
- What is the main purpose of an AI compliance audit?
An AI compliance audit ensures that AI systems comply to legal regulations, ethical standards, and risk management protocols, safeguarding organizations from penalties and reputational harm.
- Who is affected by the EU AI Act?
The EU AI Act applies to any organization deploying AI systems within the EU or affecting EU citizens, especially those operating high-risk AI applications across sectors like healthcare, finance, and law enforcement.
- How often should AI compliance audits be conducted?
AI compliance audits should be conducted regularly, especially when deploying new AI systems, updating existing models, or when regulations evolve. Continuous monitoring is recommended for high-risk applications.
- Are there penalties for non-compliance with AI regulations?
Yes, under the EU AI Act, penalties can reach up to €35 million or 7% of global annual turnover, depending on the severity of the breach and the risk category of the AI system involved.
- How can small businesses manage AI compliance effectively?
SMEs can utilize tools like the AI Act Compliance Checker, adopt best practices early in development, engage third-party auditors, and stay informed about regulatory updates to manage compliance efficiently despite limited resources.
Mastering the EU AI Act and Global AI Regulations
Mastering the EU AI Act and Global AI Regulations
Mastering the EU AI Act and Global AI Regulations